A relay 5A is an electromechanical switch that controls the opening and closing of circuits using electromagnetic induction. In simpler terms, a relays allows a low-power signal to control a higher-power device, acting like a lever that amplifies small efforts to move larger loads. This function makes HH53P Intermediate Relay 5A incredibly useful in various applications, from automobiles to industrial controls and home appliances.
When current flows through the relay’s 5A coil, it generates a magnetic field that pulls a metal armature. This movement changes the position of the contacts, allowing them to open or close the circuit—completing or breaking the connection. This design enables relays to safely manage high-power devices while using low-power control signals, making them ideal for acting as safety isolation switches.
For example, in an automobile, a small control signal from the ignition system can trigger the relay 5A to start the engine, which requires much more power than the ignition circuit can handle directly.
Features and Main Components
Relay 5A consist of several key components working together:
- Coil: Generates a magnetic field when current passes through it.
- Contacts: The moving parts that open or close the circuit.
- Spring: Ensures that contacts return to their initial position once the coil is de-energized.
- Core: Concentrates and strengthens the magnetic field generated by the coil.
These components allow relays to perform automated control tasks in various environments. Relays are valued for their ability to provide:
- Electrical Isolation: The control circuit is electrically isolated from the load circuit, ensuring safety. This isolation is crucial in protecting sensitive electronics from high-voltage circuits.
- High Reliability: Mechanical relays have long service lives with low failure rates due to their robust design.
- Versatility: Relays can handle different types of loads, whether they are DC or AC devices. This versatility makes them suitable for many industries, from consumer electronics to heavy machinery.
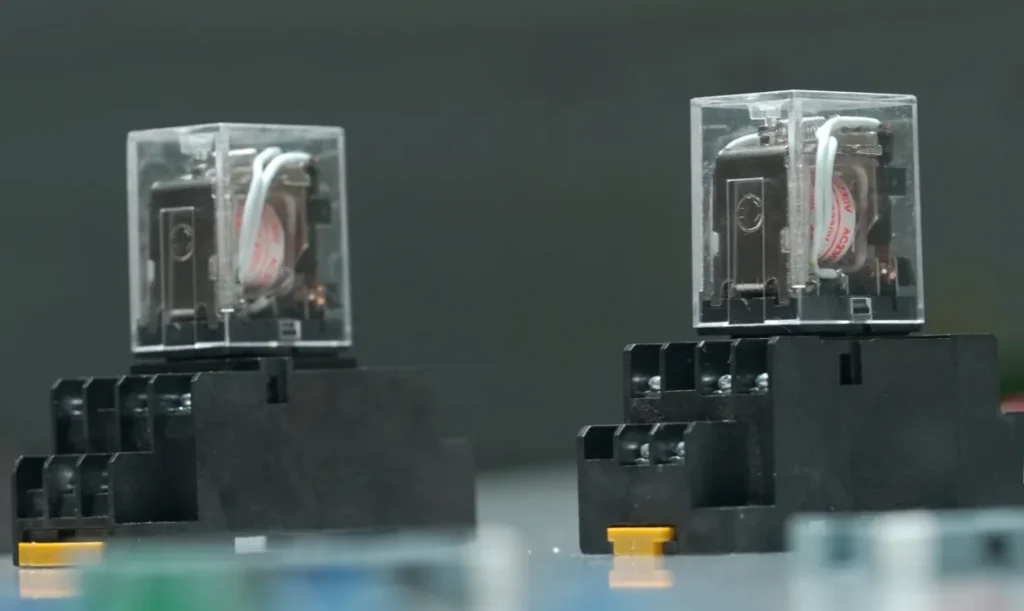
Advantages and Disadvantages of Relay 5A
Like any technology, relay 5A come with both advantages and disadvantages.
Advantages:
- High Voltage Resistance: Relay can manage high-voltage and high-power devices efficiently. For instance, they are commonly used in power distribution systems where voltages exceed 10kV.
- Excellent Isolation: The complete electrical isolation between control and load circuits provides additional safety. This feature is especially important in medical equipment or hazardous environments where electrical isolation can prevent accidents.
- Variety of Options: There are many types of relays available depending on the application—such as solid-state relays, which use semiconductors instead of mechanical parts for switching, or audio relays designed specifically for sound systems.
Disadvantages:
- Mechanical Wear: Traditional mechanical relays have moving parts that wear out over time due to friction and repeated use. This wear can reduce their lifespan compared to solid-state alternatives.
- Slower Response Time: Mechanical relays take longer to switch compared to solid-state relays, which have no moving parts and can switch in microseconds.
- Noise Issues: When mechanical relays operate, they produce an audible “click” as contacts move. In quiet environments like recording studios or medical facilities, this noise can be disruptive.
Common Types of Relay 5A
Relay 5A come in various types, each designed for specific applications. Here are some of the most common types:
- Mechanical Relays: These are the most widely used relays, relying on physical contacts to switch circuits. They are well-suited for general industrial machinery and household equipment. Their simplicity and reliability make them a go-to choice for many applications, but they do have moving parts that can wear out over time.
- Solid-State Relays: Unlike mechanical relay 5A, SSRs have no moving parts. Instead, they use semiconductor components to perform switching. This design allows them to operate silently and with much faster response times. SSRs are ideal for applications that require high-speed switching and long operational life, such as in industrial automation systems or high-frequency switching environments.
- Buchholz Relays: These specialized relays are used primarily in oil-immersed transformers to detect internal faults such as oil level changes or gas leaks. They play a critical role in transformer protection, acting as an early warning system for potential issues that could lead to catastrophic failures.
- Audio Relays: As the name suggests, these relays are commonly found in audio equipment, where they switch audio signal lines. Their ability to handle low-level signals without introducing noise makes them indispensable in high-fidelity sound systems.
These different types of relays cater to a wide variety of needs across industries—from home automation systems to complex industrial controls. For example, in India, relays are widely used across various industrial sectors, and the term “relay” translates to “रिले” (relay meaning in Hindi), reflecting their global significance.
Installation and Maintenance
Proper installation and regular maintenance are essential to ensure that relay 5A function reliably over time. Here are some key practices:
- Mounting Location: Always install relays in a dry, well-ventilated area to prevent moisture or overheating from affecting their performance. Overheating can degrade the relay’s components, leading to premature failure.
- Wiring Check: Periodically inspect the wiring for signs of wear or looseness. Loose or aging wires can cause short circuits or poor contact, which could lead to relay malfunction or even damage to connected devices.
- Cleaning and Lubrication: For mechanical relays, regular cleaning of the contacts is essential to maintain optimal performance. Dust or corrosion on the contacts can hinder electrical conductivity. Additionally, proper lubrication of moving parts can extend the relay’s lifespan by reducing friction and wear.
While solid-state relay require minimal maintenance due to their lack of moving parts, mechanical relay 5A need more frequent inspections and occasional part replacements as they experience mechanical wear over time.
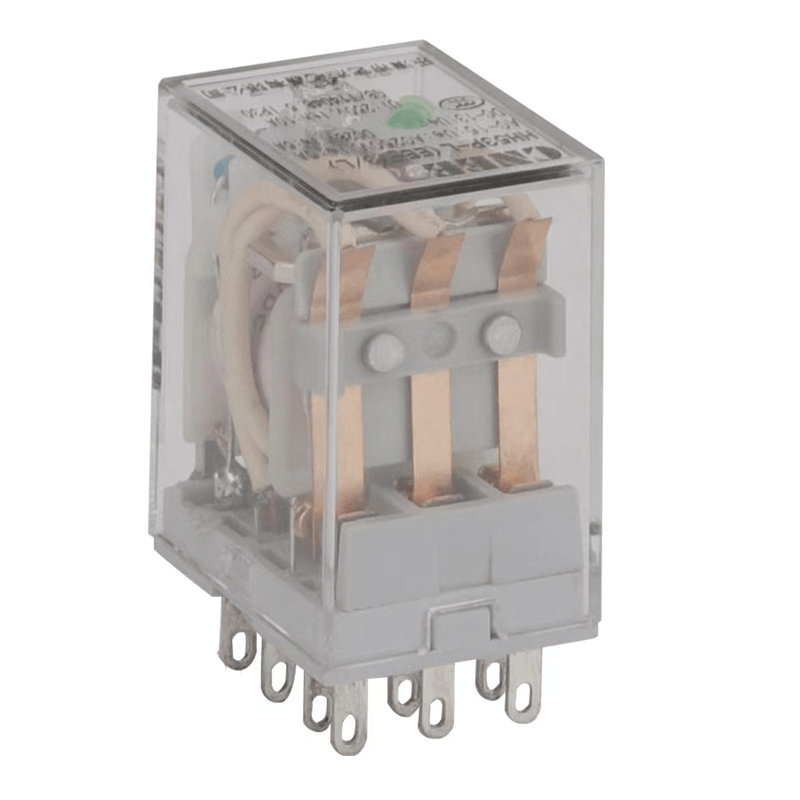
How to Choose the Right Relays 5A
Selecting the right relay 5A for your application involves considering several important factors:
- Load Type: The type of load you need to control—AC or DC—will influence your choice of relay. For high-power loads like motors or industrial equipment, solid-state relay are often preferred due to their durability and fast switching capabilities. On the other hand, for everyday household appliances with lower power demands, a standard mechanical relay is usually sufficient.
- Response Speed: If your application requires rapid switching—such as in automated manufacturing processes—solid-state relays are ideal because they operate without delay and produce no noise during operation. Mechanical relays may not be suitable for such applications due to their slower response times and audible clicking sounds when switching.
- Environmental Conditions: Harsh environments with extreme temperatures, humidity, or dust require more robust relays with higher protection ratings (e.g., IP-rated enclosures). For example, in outdoor settings or industrial plants with high exposure to moisture or contaminants, choosing a relay with enhanced environmental resistance ensures reliable performance over time.
- Cost vs. Lifespan: Solid-state relays tend to be more expensive upfront but offer longer lifespans due to their lack of mechanical parts that can wear out. Mechanical relays are cheaper but require more frequent maintenance and part replacements over their service life.
Whether you’re selecting a relay 5A for an industrial automation system or a home automation project, it’s essential to weigh these factors carefully based on your specific needs. For instance, Buchholz relays are indispensable in protecting transformers within complex industrial systems, while a simple relay module will suffice for basic home automation tasks like controlling lights or appliances.
FAQ
1. What is a relay 5A? How does it work?
A HH53P Intermediate Relay 5A is an electrical switch that controls the on/off state of a circuit through electromagnetic induction. It uses a small control signal to control high-power devices. When current passes through the relay coil, a magnetic field is generated that attracts the metal contacts, changing the on/off state of the circuit.
2. What is the difference between a mechanical relay and a solid-state relay?
Mechanical relays rely on physical contacts for switching, which can be noisy and slow to respond. Solid-state relays have no mechanical parts, can switch quickly and without noise, and are more suitable for applications that require quick response.
3. What should be paid attention to when installing and maintaining relay 5A?
When installing, choose a dry, well-ventilated location and regularly check the wiring for looseness or aging. For mechanical relays, regular cleaning of contacts and proper lubrication can extend their service life, while solid-state relays require almost no maintenance.
4. What is the main function of a Buchholz relay?
Buchholz relays are mainly used in oil-immersed transformers and are able to detect internal faults such as oil level changes or gas leaks. This early warning system is essential to prevent transformer failures.
5. How are relay 5A used in home automation?
In home automation, relays can be used to control lights, household appliances, etc. For example, a signal can be sent through a smart home system to activate the relay, thereby achieving remote control or timed switching of equipment.
6. What are the main uses of relay 5A?
Relay 5A are used to control high-power devices through low-power signals and are widely used in automobiles, industrial controls, and household appliances.
7. What are the advantages of solid-state relays?
Solid-state relays have no mechanical parts, fast response speed, no noise, and long life, making them suitable for occasions that require frequent switching.
8. Why do mechanical relays make noise?
When a mechanical relay switches, the movement of the physical contacts will make a “clicking” sound, which is the result of mechanical action.
9. How to extend the life of a mechanical relay?
Regular cleaning of the contacts and proper lubrication can reduce wear and extend the service life of a mechanical relay.
10. What is the role of an audio relay?
Audio relays are used to switch audio signal lines to ensure that audio equipment switches seamlessly between different signal sources.


