Selection and testing of Electromagnetic relay
As a core component in industrial control and power systems, the performance and reliability of electromagnetic relays directly affect the safety and stability of equipment. With the increasing demand for automation and intelligence in modern industry, the selection and testing of electromagnetic relays have become a key link in engineering design.
However, faced with complex working environments and diverse load conditions, how to scientifically select relays with adapted parameters and verify their durability, contact performance and anti-interference capabilities through systematic testing is still a challenge facing engineers. Starting from practical applications, this article discusses the selection criteria, core test methods and solutions to common problems of electromagnetic relays, providing a reference for optimizing system design and extending equipment life.
How to choose the right Electromagnetic relay according to the load
When selecting an electromagnetic relay, factors such as contact and load type, coil parameters, and environment should be considered.The main factors include:
Contact capacity: Select the appropriate contact capacity according to the current and voltage of the load to ensure that the relay can withstand the load.
Load type: Different loads (such as resistive, inductive or capacitive) have different requirements for relays. Inductive loads need to consider the arc resistance of the contacts.
Coil parameters: Select the appropriate coil rated voltage according to the voltage of the control circuit to ensure that the relay can operate reliably under normal working conditions.
Environmental conditions: Consider factors such as temperature and humidity in the working environment and select relays with good environmental resistance.
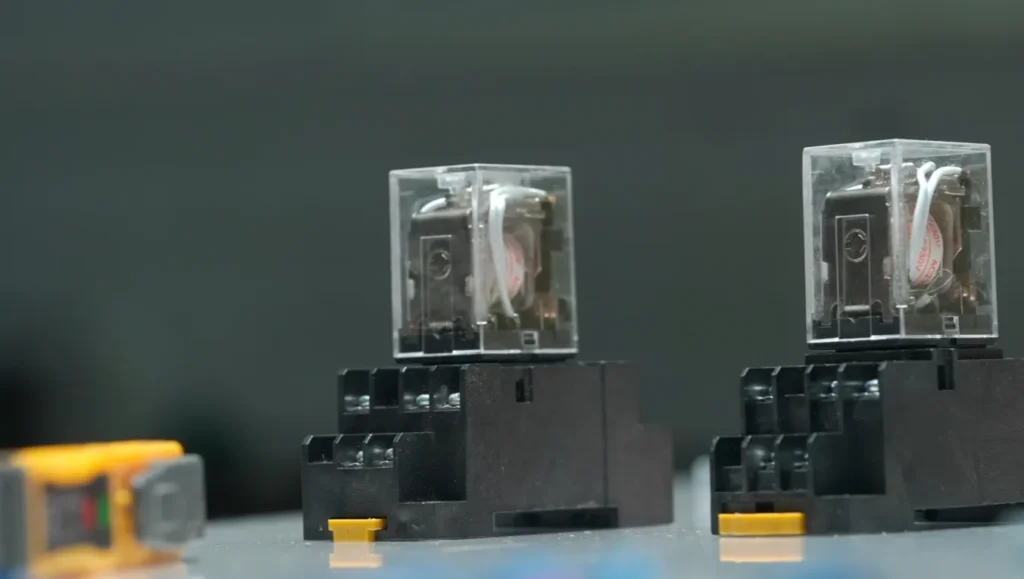
Structural differences between different types of relays
There are many types of relays, and their structural differences are mainly reflected in the following aspects:
H-type: the contacts are open when the coil is not energized, and the contacts are closed when energized.
D-type: the contacts are closed when the coil is not energized, and the contacts are open when energized.
Z-type: contains one moving contact and two static contacts, and the switching is achieved by turning the coil on and off.
Reed relay: uses the action of the reed sealed in the tube to open and close the circuit, and has a fast response speed.
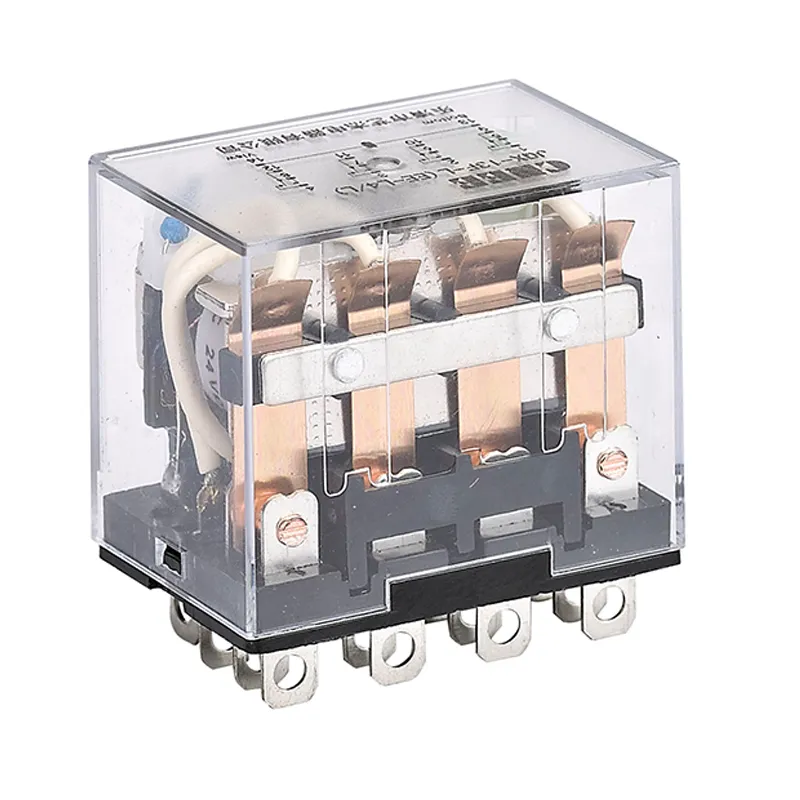

Testing methods for electromagnetic relay contacts and coils
Methods for testing contacts and coils include:
- Contact test: Use a multimeter to measure the conductivity between contacts to ensure good contact. Check for burnout or oxidation.
- Coil test: Determine whether the coil is normal by measuring its DC resistance. Under normal circumstances, the coil should have a certain resistance.
- Bounce time test: Use a special test device to measure the contact bounce time to evaluate the performance of the relay.
Wiring methods for electromagnetic relay
Control terminal wiring: There are usually two terminals, A1 and A2, for connecting control signals. Make sure the wiring is firm and avoid looseness.
Load terminal wiring: Connect to the corresponding normally open or normally closed contacts according to load requirements.
Pay attention to polarity: For DC relays, pay attention to the polarity of the control terminal and the load terminal to avoid affecting normal operation.
Judgement and troubleshooting of common faults
Common faults and their troubleshooting methods include:
Coil fault: If the coil is open or short-circuited, it can be confirmed by measuring the DC resistance and repaired or replaced.
Contact fault: When the contact is sticky or burned, the contact should be cleaned or replaced. Check whether it is caused by overload and adjust the use conditions.
Mechanical jam: Check and remove foreign matter to ensure that the mechanical part operates flexibly.
Abnormal noise: It may be due to poor contact between the dynamic and static iron cores, which should be cleaned and leveled.
The selection and testing of electromagnetic relays is a multi-dimensional trade-off process, which requires comprehensive consideration of key indicators such as load characteristics, environmental adaptability, electrical parameters (such as contact capacity, coil voltage) and mechanical life. Standardized tests (such as mechanical durability tests, temperature rise tests, and insulation performance verification) can effectively predict the performance of relays under extreme working conditions and avoid contact adhesion, coil overheating or premature failure caused by improper selection.
In addition, combining industry standards (such as IEC, UL) with actual on-site needs to formulate dynamic maintenance strategies can significantly improve system reliability. In the future, with the development of new materials and intelligent monitoring technologies, the selection and testing of electromagnetic relays will become more accurate and efficient, providing more solid technical support for industrial automation.
Zhejiang Hangwang Electrical Technology Co., Ltd. was established in 2022 and is located in China. It is a modern enterprise that has introduced international advanced technology and equipment technology, focusing on the research and development, manufacturing, production, sales and service of electronic relays in the industrial control field. We provide a full range of high-quality relay products from small to high power to meet your various needs in the fields of industrial automation, new energy, etc. Choosing Hangwang means choosing innovation, quality and excellent service.